ISA (International Standard Atmosphere): Atmospheric model for standard temperature, pressure at different altitudes, aiding in flight planning and aircraft performance.
ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization): UN agency setting international aviation standards, including meteorology and atmospheric models.

ICAO has defined ISA (International Standard Atmosphere) conditions as follows:
ISA Conditions
| Condition | Value |
| Air | Dry air with 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 0.03% Carbon Dioxide, 0.9% Argon and other gasses. |
| Temperature at MSL | 15°C (288.15 K) |
| Pressure at MSL | 1013.25 hPa (29.92 inHg) |
| Density at MSL | 1225 g/m³ |
| Acceleration due to Gravity | 9.8 m/s² |
| Lapse Rate | Up to 11 km – 1.98°C/1000 feet or 6.5°C/km (temperature decreases) 11 – 20 km – Constant -56.5°C 20 – 32 km – 0.3°C/1000 feet or 1°C/km or (temperature increases) Above 32 km – Constant -44.5°C |
ISA assumes calm and dry air with no water vapor and standard atmospheric conditions.
- Lapse Rate only applies up to 11 km (36,089 ft), after which the lapse rate changes.
- These conditions are used as a baseline for flight planning and aircraft performance calculations.
💡 Did you know?
The atmosphere is heated by the Earth’s surface, not directly by the Sun.
The Sun’s shortwave radiation heats the Earth, which then emits longwave radiation that warms the atmosphere.
| Pressure | Approximate Level |
| 200 hPa | 40,000 ft |
| 300 hPa | 30,000 ft |
| 400 hPa | 24,000 ft |
| 500 hPa (~50%) | 18,000 ft |
| 700 hPa | 12,000 ft |
| 850 hPa | 5000 ft |
| 1013.25 hPa | Mean Sea Level |
🧠 To Memorize, Remember
- At 500 hPa, pressure is about half of sea level pressure (1013.25 hPa) at 18,000 ft.
- At 300 hPa, the altitude is 30,000 ft, linked by the number “3.”
- Each 100 hPa drop corresponds to an approximate increase of 6,000 ft.
- At 200 hPa, remember 2 times 2 equals ‘4’ of 40,000 ft.
Lapse Rate
Lapse rate by definition is fall in temperature with height. If the temperature rises with height, it is considered a negative lapse rate.
For example:
- The lapse rate is positive up to 11 km — True.
- The lapse rate can be negative from 20 km to 30 km — True.
ISA Deviation = Actual – ISA
In Jet Standard Atmosphere, the lapse rate is 2°C/1000 ft.
In actual temperature, the lapse rate could assume any value.
Earth’s Atmosphere
- The Earth’s atmosphere extends approximately 480 km in thickness.
- The atmosphere is well-mixed (homogeneous) up to about 80 km due to Earth’s gravitational force. Above this altitude, it becomes heterogeneous.
- 50% is within 6 km
- 75% is within 10 km
- 80% is within 16 km
- 99% is within 35 km
Composition of Air (by Volume)
- 78% Nitrogen,
- 21% Oxygen,
- 0.03% Carbon Dioxide,
- 0.9% Argon and other gasses
All others are traces (Water vapor is a trace gas, also called a variable gas.)
Nitrogen: Oxygen Ratio
| By Volume (N₂:O₂) | 4:1 |
| By Mass (N₂:O₂) | 3:1 |
📝 Memorization Tip
- Remember it’s always N₂:O₂.
- For volume, think of the “V4” engine in Audi, which represents the 4:1 ratio.
- For mass, simply remember it as 3:1.
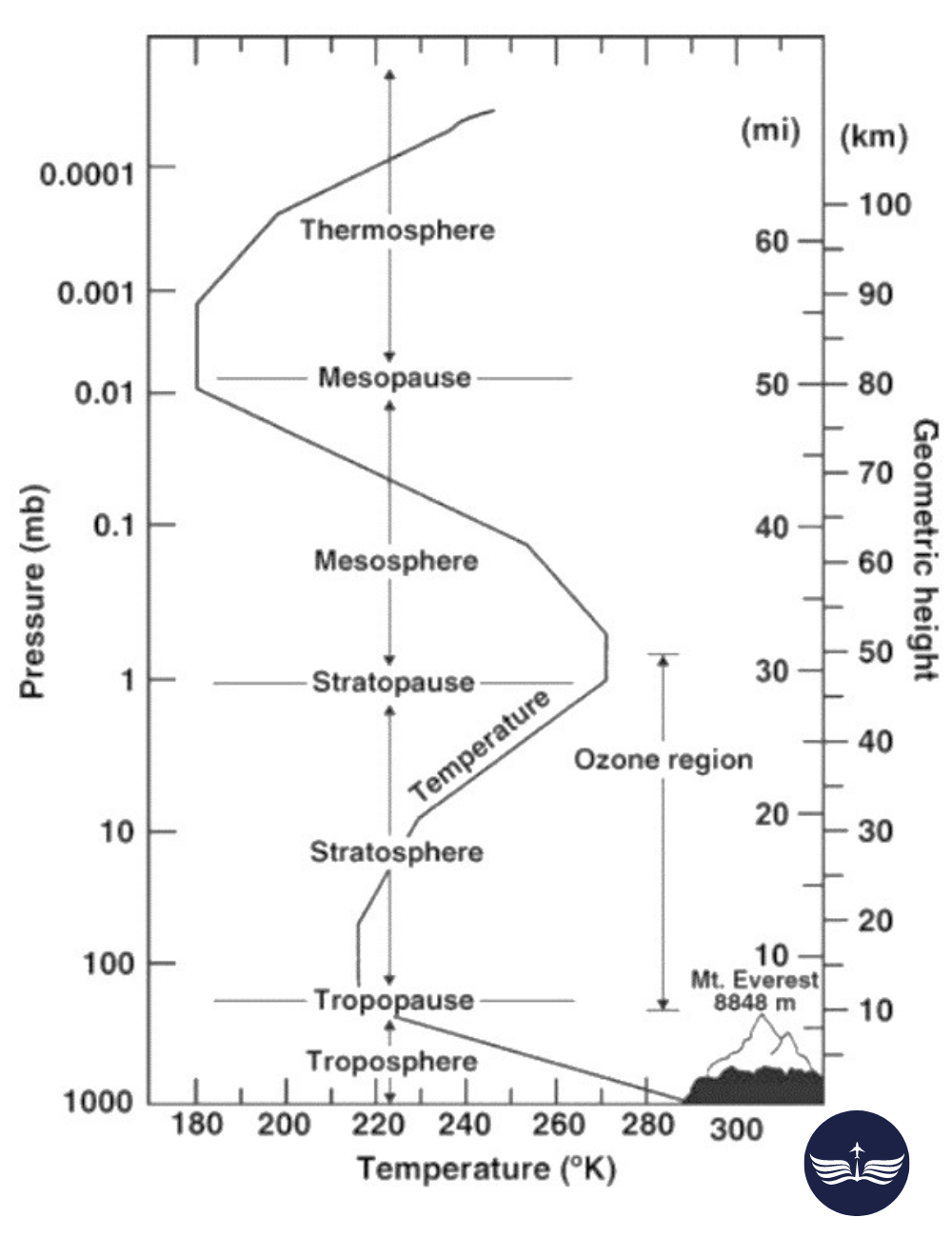
Layers of Atmosphere
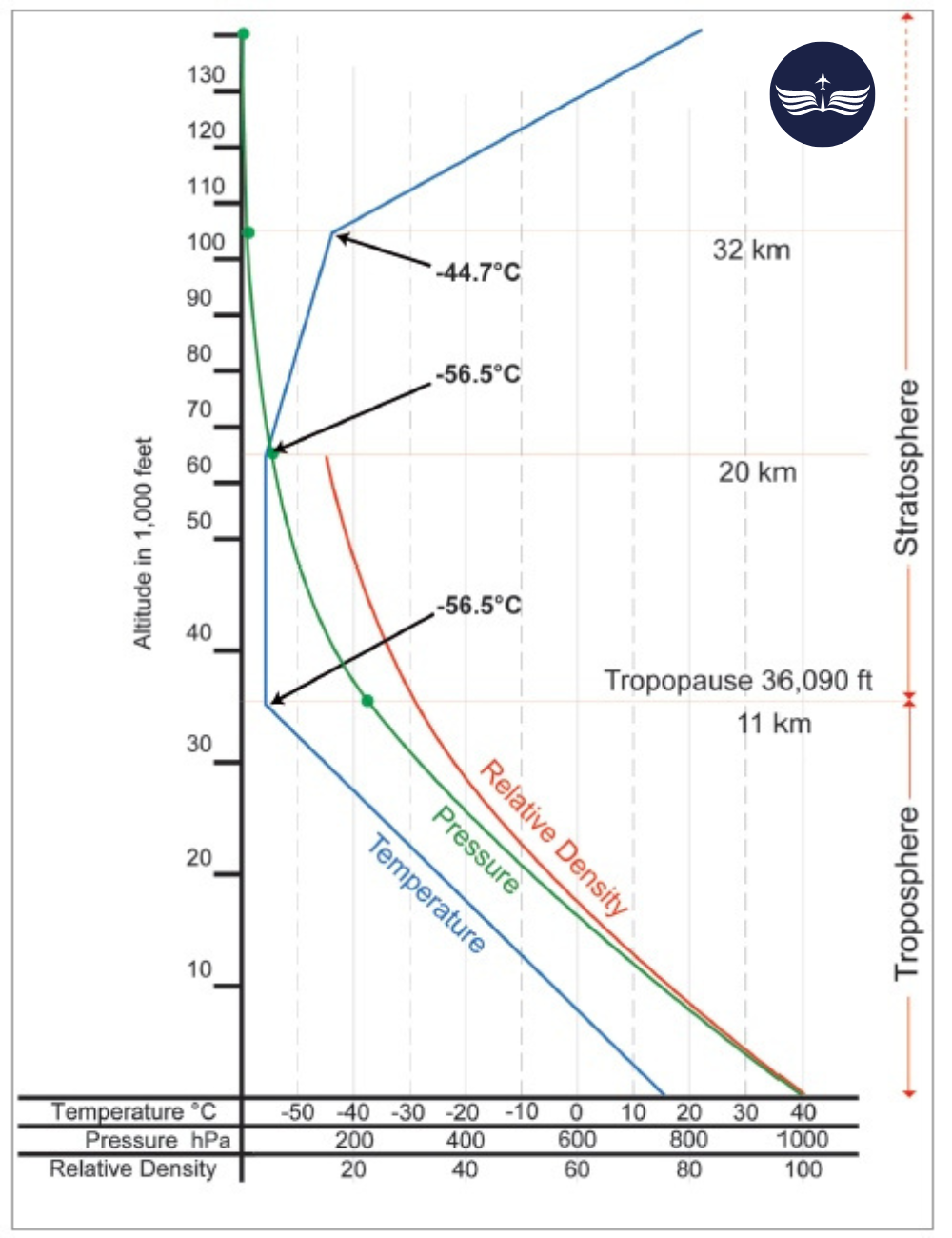
Troposphere
- Height varies with latitude (16-18 km at the equator, 8-10 km at poles).
- Temperature decreases with altitude (6.5°C per 1000m – standard lapse rate).
- Contains 75% of the atmosphere’s mass, where weather phenomena occur.
Stratosphere
- Extends to about 50 km.
- Contains the ozone layer, temperature increases with height due to ozone absorption of UV radiation.
Mesosphere, Thermosphere, and Exosphere: Higher layers with specialized properties.
Gasses
- Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), and other gasses (1%) like Argon, Carbon Dioxide, etc.
- Water vapor varies (up to 4% by volume in tropical regions).
Carbon dioxide absorbs infrared radiation, affecting global temperature (important in greenhouse effect concepts).
[sc name=”promoting-quiz-on-wingedpilot” ][/sc]
