#1. Lowest Layer of atmosphere is
Quick Facts:
- Extends from surface to ~15 km
- Contains ~75% of atmospheric mass
- All weather phenomena occur here
- Tropopause is the boundary above it
- Stratosphere lies above the tropopause
#2. Height of Tropopause at equator is
- Tropopause is highest at the equator (16–18 km)
- Lowest at the poles (8–10 km)
- Varies with latitude and temperature
- Acts as a boundary between troposphere and stratosphere
#3. Height of Tropopause at poles is
- Lowest at the poles due to colder temperatures
- Higher in tropics (16–18 km)
- Acts as a cap for most weather systems
- Separates troposphere from stratosphere
#4. Higher the surface temperature_______ would be the tropopause
- Warm air → Tropopause rises
- Cold air → Tropopause lowers
- That’s why it’s higher at the equator, lower at the poles
#5. Height of tropopause
- Higher at the equator (16–18 km)
- Lower at the poles (8–10 km)
- Controlled by temperature differences
- Warmer air = higher tropopause
#6. Atmosphere is heated by
- Sun heats the Earth’s surface first
- Surface then radiates heat upward
- Atmosphere is indirectly heated from below
- That’s why temperature decreases with height in the troposphere
#7. Tropos means
- From Greek “Tropos” = Turning or mixing
- Refers to constant motion in this layer
- Supports weather, winds, and convection currents
- That’s why weather happens in the troposphere
#8. CO₂ and H₂O are also called
Water vapor, CO₂, O₃, methane, and some other gases are transparent to solar radiation but partially absorb terrestrial radiation. They then re-radiate this energy, trapping heat and keeping Earth warmer.
#9. Stratosphere is
The stratosphere is generally stable. This stability is due to the fact that in the stratosphere, temperature increases with altitude (a phenomenon called temperature inversion). In a stable atmosphere, warmer air is located above cooler air, which suppresses vertical air movement, making the stratosphere resistant to turbulence and vertical convection.
#10. Tropopause is discontinuous at about
The tropopause is discontinuous at about 40º latitude. This discontinuity occurs because the height of the tropopause varies with latitude, being higher over the equator and lower over the poles.
#11. Most of atmospheric mass is contained in
#12. Stratosphere extends from Tropopause to

#13. The middle atmosphere layer with temperature inversion and stability
Inversion refers to an increase in temperature with height.
Inversion occurs due to the absorption of ultraviolet rays by ozone.
The stratosphere is a stable weather environment due to low humidity.
#14. Mother of Pearl clouds occur in
Remember:
N in M: Noctilucent clouds occur in the mesosphere.
M in S: Mother-of-pearl clouds (nacreous) occur in the stratosphere.
#15. The temperature of ISA at 17km is
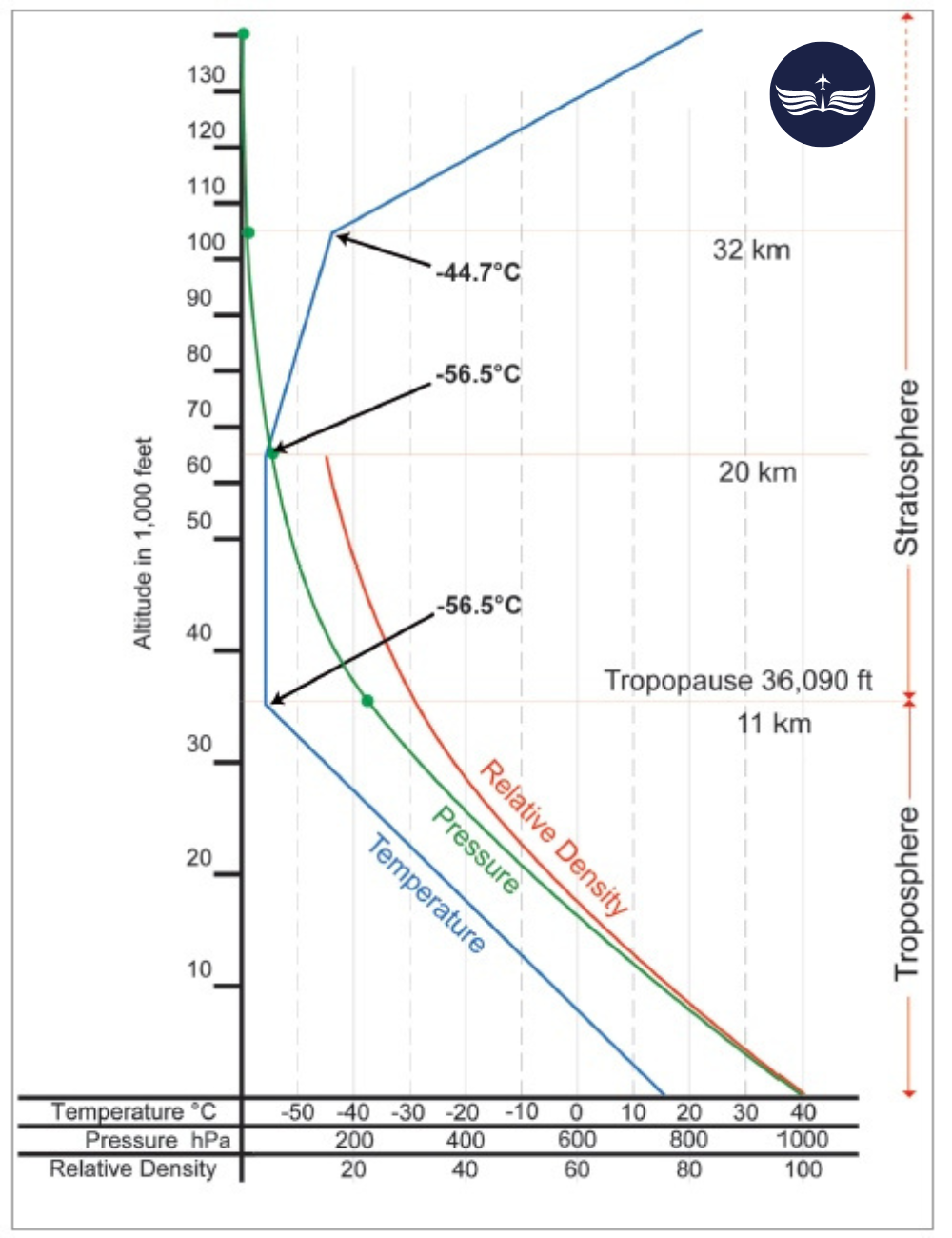
The temperature remains constant at -56.5°C from 11km – 20km.
#16. By volume, the approximate ratio of O² to N² in the atmosphere is
W3 for weight
V4 for volume
#17. By weight, approximate ratio of O² and N² in the atmosphere is
W3 for weight
V4 for volume
#18. By volume, the proportion of CO² in the atmosphere is
Nitrogen: 78.09%
Oxygen: 20.95%
Argon: 0.93%
Carbon dioxide: 0.035%
#19. In ISA, the mean sea level temperature is
The ICAO ISA is defined as follows:
- A mean sea level (MSL) temperature of 15°C
- An MSL pressure of 1013.25 hPa
- An MSL density of 1225 g/m³
- A lapse rate of 6.5°C/1km (1.98°C/1000 ft) up to 11 km (36,090 ft)
- A constant temperature of -56.5°C from 11 km (36,090 ft) to 20 km (65,617 ft)
- An increase in temperature of 0.1°C/100m (0.3°C/1000 ft) from 20 km (65,617 ft) to 32 km (104,987 ft)
#20. Maximum concentration of ozone is at a height of
Ozone forms in the upper atmosphere. It absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun, raising the temperature. O₃ molecules then become heavier, sink, and accumulate in the lower levels. Ozone protects us from the harmful effects of UV radiation. Appreciable O₃ is found between 10 and 50 kilometers, with the maximum concentration at 20 to 25 kilometers.
#21. Additional oxygen is needed while flying above
Due to the rapid decrease in oxygen with increasing altitude, supplemental oxygen is needed at 10,000 feet.
#22. CO² and H²O keep the atmosphere
Water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO₂), ozone (O₃), methane, and several other gases are transparent to solar radiation but absorb terrestrial radiation partially. This absorption leads to the re-emission of energy, trapping heat and keeping Earth warmer. These gases are therefore known as greenhouse gases.
#23. Noctilucent clouds occur in
N in M: Noctilucent clouds in mesosphere.
#24. Temperature at 2 km is 05°C. What is the ISA deviation? (Hint: Actual – ISA)
As per ISA conditions, the lapse rate is 2°C per thousand feet of climb or 6.5°C per thousand meters. At 2 km, the reduction should be 15° – 13° = 2°C. However, it’s 5°C, which is higher by 3°.
#25. Pressure at MSL is 1002.25 hPa. Find the ISA deviation. (Hint: Actual-ISA)
Pressure should be 1013.25 hPa, but there is a deviation of -11 hPa.
#26. In the actual atmosphere, the temperature at 19 km is -60°C. Find the ISA deviation?
In the lower stratosphere, the temperature is -56.5°C. However, it’s -60°C, so there is a deviation of -3.5°C.
#27. Nacreous clouds occur in
Remember: N in M: Noctilucent clouds in mesosphere. M in S: Mother-of-pearl clouds (nacreous) in Stratosphere.
#28. The atmosphere up to 80 km has a nearly similar composition and is called the Homosphere. Its uniform composition is due to
#29. Half of the atmospheric air mass is contained _____ below
- 50% is within 6 km
- 75% is within 10 km
- 80% is within 16 km
- 99% is within 35 km
#30. In the jet standard atmosphere, the Lapse Rate is
The lapse rate in the jet standard atmosphere is 2°C per 1000 feet.
#31. The rate of fall of temperatures with height is called
A lapse rate is the rate at which temperature decreases with altitude.
#32. In the actual atmosphere, the lapse rate could
The lapse rate in the actual atmosphere can vary depending on various factors.
#33. Tropical Tropopause extends from the equator to Lat.35° – 40°. Over India, it is at
The tropical tropopause extends from the equator to latitudes 35° – 40°. Over India, the tropopause is typically found at around 16-17 kilometers (52,000-56,000 feet) above sea level.
#34. Lapse rate in the troposphere is produced by _____ and in the stratosphere by ______
In the troposphere, the lapse rate is primarily due to rising air and solar radiation heating the ground. In the stratosphere, the lapse rate is negative due to the absorption of ultraviolet radiation by ozone.
#35. Most of the water vapor in the atmosphere is confined up to
W.V. is negligible above 30,000 feet and at the poles.
#36. Negative lapse rate of temperature is
Inversion occurs when temperature increases with altitude, often due to factors like radiative cooling or ozone absorption.
#37. In ICAO ISA, the atmosphere is assumed to be isothermal
In the ICAO ISA, the atmosphere is assumed to be isothermal between 11 and 20 kilometers.
#38. One of the characteristics of our atmosphere is
Air is a poor conductor of heat due to the spacing between its molecules.
#39. Heat transfer in the atmosphere is maximum due to
In the troposphere, heat transfer is primarily due to latent heat, which involves the phase changes of water.
#40. The knowledge of the height of tropopause is important for a pilot because
Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, so understanding the tropopause height is crucial for pilots.
#41. In the ISA atmosphere, the tropopause occurs at a height of
According to the ICAO ISA, the tropopause occurs at an altitude of 11 kilometers.
#42. There is a reversal of temperature in the atmosphere at 8 km because
Since temperature decreases with height it goes to follow that the temperature at the tropopause is controlled by its height. At poles tropopause stops at 8 km and temperature starts increasing , whereas at equator, where tropopause extends till 16 km above 8km temperature further reduces as per lapse rate.
#43. Above 8 km the lower temperatures are over
Since temperature decreases with height it goes to follow that the temperature at the tropopause is controlled by its height. At poles tropopause stops at 8 km and temperature starts increasing , whereas at equator, where tropopause extends till 16 km above 8km temperature further reduces as per lapse rate
#44. Troposphere is generally
Most of the water vapour is in the troposphere because of which there are weather creating clouds and hence troposphere is unstable
#45. Most of the transfer of heat in the atmosphere is due to
[INSERT_ELEMENTOR id=”2087″]




